Carborane derivatives as inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes
INTRODUCTION:
Human carbonic anhydrases (CAs) play important roles in many pathological processes and several CA isoenzymes thus represent diagnostic and therapeutic targets. The development of certain isoform-specifi c sulfonamide inhibitor is still an important task in current medicine.
TECHNOLOGY (INVENTION) DESCRIPTION:
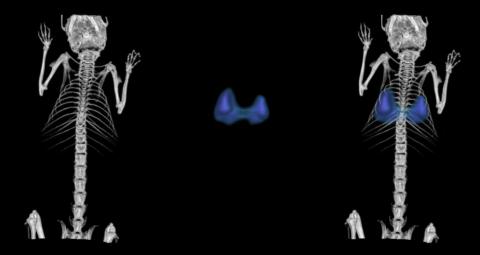
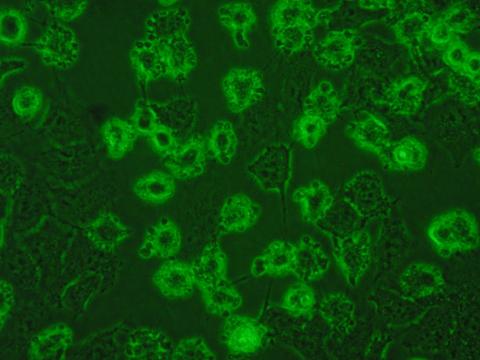
We have developed unique selective CAIX inhibitors with anticancer properties based on carborane scaffold to structure-assisted design of novel and original inhibitors targeting therapeutically relevant isoenzymes of human carbonic anhydrase.
ADVANTAGES OVER EXISTING SOLUTIONS:
Novelty, in brief, is represented by the intended elaboration of carborane, heteroborane and metallaborane compounds as active-site inhibitors of CA isoenzymes. All currently used inhibitors anhydrase inhibitors contain a sulfonamide or a sulfamate moiety connected to so called ‘ring structure’ which is usually a 5- or 6-membered aromatic ring or conjugated ring system containing nitrogen, oxygen, and/ or sulfur heteroatoms. The ‘ring structure’ bears characteristics or functionality which modulates the affi nity toward certain CA isoform. The use of three-dimensional boron cluster is a novel approach in development of isoform-specifi c CA inhibitors. Selected sulfamides incorporating cluste
DEVELOPMENT STATUS (STAGE):
Laboratory scale, data on cell lines, crystal structure, limited ADME/Tox data, in vivo pharmacology and pharmacodynamic
PUBLICATIONS:
IP PROTECTION STATUS:
Patent protection: WO 2013/060307 EP 2771015 US 2014/303390
TECHNOLOGY / IP OWNERS :
Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Czech Academy of Sciences Institute of Molecular Genetics, Czech Academy of Sciences Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Czech Academy of Sciences Palacky University Olomouc
More information
More information is available upon signing a CDA / NDA (Confidential Disclosure Agreement / Non-Disclosure Agreement)