Photoactive nanofiber materials with antibacterial and antiviral effect.
INTRODUCTION:
Currently, it is possible to prepare nanofiber materials using industrial-scale electrospinning devices. Introducing photoactive compounds, nanomaterials for several applications in medicine, including coverings (e.g., wound dressings and plasters), surgery supplements (e.g., surgery masks), and disinfection of aqueous media can be created.
TECHNOLOGY (INVENTION) DESCRIPTION:
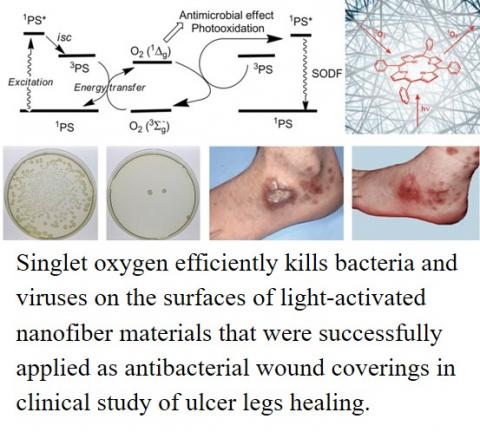
Photoactive polymer nanofiber materials (such as membranes) prepared by electrospinning with encapsulated and/or externally attached photosensitizers and/or NO-photodonors generating highly cytotoxic singlet oxygen and NO radical upon activation by visible light were developed. Such materials have ability to detain bacteria or other pathogens on the nanoporous surfaces and exhibit very strong antibacterial and antiviral effect upon irradiation by visible light (daylight).
ADVANTAGES OVER EXISTING SOLUTIONS:
The high surface area and the nanoporous structure of nanofiber material modified by combination of two types of photoactive compounds offer the great advantage to provide a high concentration of photoactive compounds and prevent bacteria and other pathogens from passing through the nanofiber materials. The pathogens are detained on the surface and killed by the photogenerated singlet oxygen, NO radical, or both. Especially, singlet oxygen efficiently kills bacteria, non-enveloped polyomaviruses and enveloped baculoviruses on the surfaces of such nanofiber materials. NO radical, in contrary, can ensure the disinfection in the space.
DEVELOPMENT STATUS (STAGE):
Nanofiber materials activated by light were successfully applied as antibacterial wound coverings in clinical study.
PUBLICATIONS:
Jiří Mosinger, Kamil Lang, Pavel Kubát: Photoactivatable Nanostructured Surfaces for Biomedical Applications. Top Curr Chem (2016) 370: 135–168. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-22942-3_5
IP PROTECTION STATUS:
-
TECHNOLOGY / IP OWNERS :
Charles University, Faculty of Science, Ovocný trh 3-5, Prague 1, Czech Republic
More information
More information is available upon signing a CDA / NDA (Confidential Disclosure Agreement / Non-Disclosure Agreement)