S.M.A.R.T. neurosteroids in the treatment of neuropathic pain
INTRODUCTION:
Neuropathic pain is an indication that currently affects about 8 million people worldwide, with the market size of about $3B and expected growth to $8B in 2026. However, treatments for this indication are lacking, and only 30% of patients will see 30% efficacy from the drugs prescribed.
TECHNOLOGY (INVENTION) DESCRIPTION:
Neurosteroids are endogenous steroids that produce rapid effects on neuronal excitability and synaptic function. In general, the effect of neurosteroids is mediated by interactions with ligand-gated ion channels. We have synthesize and screen S.M.A.R.T. Steroids – Steroidal Molecules As Rapid-acting Therapeutics. These compounds have neuroprotective effect, in both in vitro and in vivo models of neurodegeneration, and show neuroprotective properties and minimal side effects in animal models of several neurological diseases. Primarily, our S.M.A.R.T. steroids were designed as modulators of the NMDA receptors; nevertheless, we have indentified new and relevant targets in the field of neuropathic pain (more information is available upon signing a CDA/NDA).
ADVANTAGES OVER EXISTING SOLUTIONS:
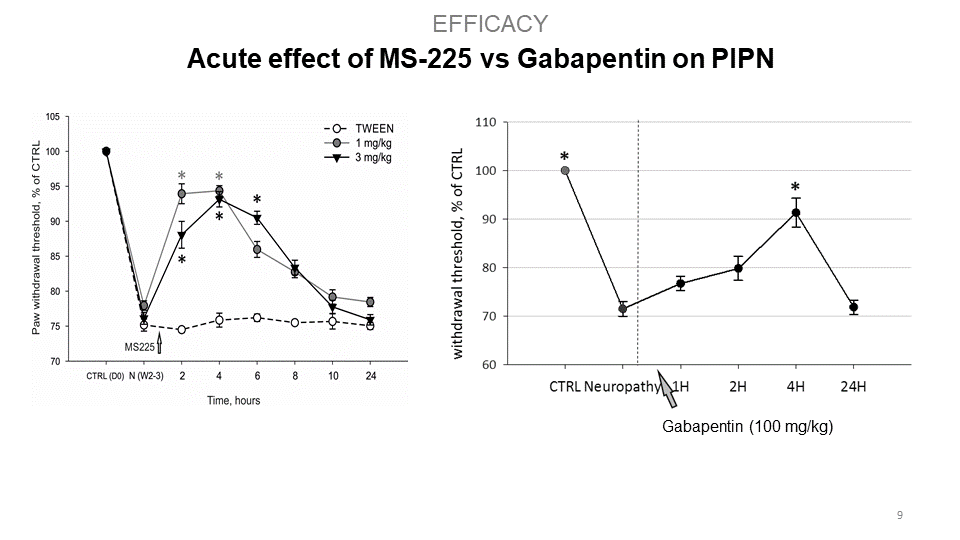
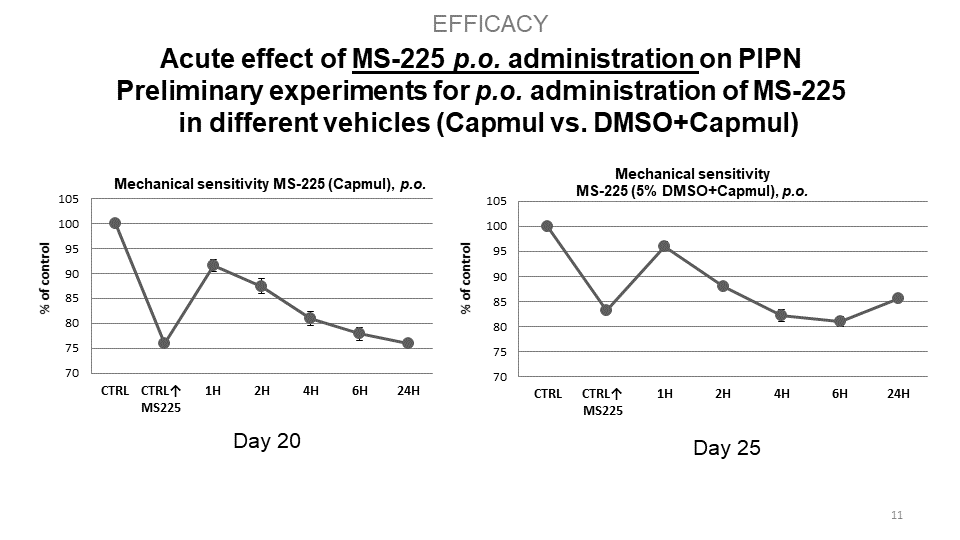
S.M.A.R.T. neurosteroids are very potent molecules with effects on crucial processes in the nervous system in general. By targeting several different receptor systems, they are able to reduce negative changes in the central nervous system, which in turn could prevent the development of central sensitization and chronic pain states. Interestingly, compounds MS225 demonstrate superior effect to Gabapentin. Moreover, S.M.A.R.T. neurosteroids display minimal or no adverse hepatic effect, cross blood-brain-barrier, are available after p.o. administration, and have no psychomimetic effects at therapeutic doses.
DEVELOPMENT STATUS (STAGE):
Preclinical stage – in vitro and in vivo testing, lead optimization, pharmacokinetics, toxicology.
PUBLICATIONS:
Krausova et al.: J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61: 4505-4516. Adla et al.: Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1299. Bukanova et al.: Neurochem. Int. 2018, 118:145-151. Vyklicky et al.: Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11: 110. Vyklicky et al.: Journal of Neuroscience 2016, 36(7):2161-2175. Vyklicky et al.: Scientific Reports 2015,18(5):10935. Slavikova et al.: J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59(10): 4727-4739. Kudova et al.: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015,58:5950-5966. Borovska et al.: British Journal of Pharmacology 2012, 166(3):1069-1083.
IP PROTECTION STATUS:
US 10017535;AU 2015309371;JP6437636(B2);US 8575376;US 8575376;EP 2435463;EP 2675821.
TECHNOLOGY / IP OWNERS :
Institute of Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry of Czech Academy of Sciences (50%) Institute of Physiology of Czech Academy of Sciences (50%)
More information
More information is available upon signing a CDA / NDA (Confidential Disclosure Agreement / Non-Disclosure Agreement)