Small molecules as effective HSD17beta1 inhibitors in cancer treatment
INTRODUCTION:
17βHSD1 an enzyme that has been known to play a pivotal role in tissue-specific estradiol (E2) synthesis, a very potent hormone, which regulates the expression of a variety of genes by binding to estrogen receptors (ER) and thus it plays a crucial role in the physiological as well as pathological proliferation and differentiation of the target cell
TECHNOLOGY (INVENTION) DESCRIPTION:
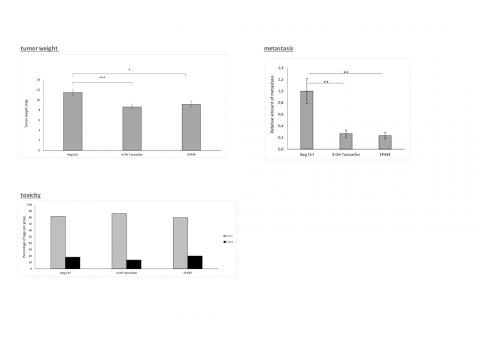
17βHSD1 affects breast cancer cell proteome and modulates expression of several genes at both mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, it is associated with an increased risk of cell migration and cancer relapse. Therefore, regulation of 17βHSD1 should be considered as potential novel endocrine therapy. We have successfully developed highly potent and specific non-estrogenic inhibitors of 17βHSD1. The efficacy of these compounds has been shown in in vitro and in vivo testings. The inhibition of E1 to E2 conversion after application of lead our lead compound has been demonstrated, furthermore we have evidence that our lead compound EP449 inhibits tumor growth and metastases forming on an egg-based T47D tumor model.
ADVANTAGES OVER EXISTING SOLUTIONS:
Our lead compound is specifically inhibiting the HSD17 enzyme, but not the ER which is still available for signaling. It has shown to be effective at a lower concentration than tamoxifen when compared in a xenograft egg-model. Our molecule could be used in pre- and post-menopausal women.
DEVELOPMENT STATUS (STAGE):
preclinical testing
PUBLICATIONS:
no publications
IP PROTECTION STATUS:
CZ2016-342 7.6.2016 PCT/CZ2017/050022 granted in CZ
TECHNOLOGY / IP OWNERS :
the technology is owned by: IOCB, IMTM, IMG and Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen

More information
More information is available upon signing a CDA / NDA (Confidential Disclosure Agreement / Non-Disclosure Agreement)